A secondary infection that occurs during antimicrobial therapy caused by overgrowth of drug-resistant residents of the microbiota. Biology questions and answers.
An infection by an extremely virulent microbe d.

. One reason to avoid taking unnecessary antibiotics is that antibiotic treatment puts you at risk for additional infections - so called superinfections. Multiple Choice Microbes that cannot be cultured are not alive and therefore have no significance in human health and disease. More severe infection rapid onset.
Maternal transfer of antibody with breast. All of the following symptoms are evidence of a superinfection except. 1 the overall medical condition of the patient 2 the nature of the microorganism causing the infection 3the antibiotic susceptibility profile of the microorganism causing the infection.
Most antihelminthic drugs function by. Microbes in the body have fewer resources after the person dies which increases competition. An infection that occurs due to the overgrowth of other potentially pathogenic microbes during or after initial antimicrobial therapy c.
Please select the 3 most important considerations in selection and administration of antimicrobial drug therapy. 1 answers 2 15 points a 10 points Compute the line integral s fxy ds of the scalar. An antibiotic that disrupts the normal flora can cause.
Which of the following statements best describes why. When a patients immune system reacts adversely. C 0 5 points How does your answer change if I reverse the orientation.
All the microbes that were living inside the persons body die when the person dies. 1 the overall medical condition of the patient. Answered Aug 13 2019 by sdrivers1.
If the pathogen causing an infection has been identified it is best to use a narrow-spectrum antimicrobial and minimize collateral. Assessment Saved Help Save Exit Please choose the statement which best explains the significance of microorganisms not being culturable. Answer the following statement true T or false F molecular-and-microbiology.
A weakening the worms so they can be flushed out by the intestine. A scientist discovers that a soil bacterium he has been studying produces an antimicrobial that kills gram-negative bacteria. Be Antibiotics Aware is the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions CDC national educational effort to help improve antibiotic prescribing and use and combat antibiotic resistance.
Presence of natural killer NK cells c. B inhibiting worm metabolism. For example some narrow-spectrum drugs only target gram-positive bacteria whereas others target only gram-negative bacteria.
2 the nature of the microorganism causing the infection. Which of the following best describes acquired immunity. Such infections are unrelated to the first infection for which the antibiotic was originally taken.
When she tests the antimicrobial properties of this new version she finds. Choose the statement that best describes superinfection. Choose the letter a statement that best describes the p.
A the teeth to turn brown. Antibiotic resistance is one of the most urgent threats to the publics healthAntibiotic resistance happens when germs like bacteria and fungi develop the ability to defeat the drugs. Please select the 3 most important considerations in selection and administration of antimicrobial drug therapy.
All of the following symptoms are evidence of a superinfection except. Microbial populations grow and spread to different areas of the body after the person dies. No longer restricted to one body site.
A narrow-spectrum antimicrobial targets only specific subsets of bacterial pathogens. Microbes that cannot be cultured may be the. 2 15 points a 10 points Compute the line integral s fxy ds of the scalar function over the oriented curve.
For example bacterial infection may occur in patients with viral respiratory disease or a chronic hepatitis B carrier may become infected with hepatitis D virus. An infection with an extensively drug-resistant microbe b. An infection with an extensively drug-resistant microbean infection that occurs due to the overgrowth of other potentially pathogenic microbes during or after initial antimicrobial therapyan infection by an extremely virulent microbe an infection caused by multiple species of microbes synergistically contributing to the infectious process nclex.
An infection that has spread to multiple body sites and tissue fluids. She isolates and purifies the antimicrobial compound then chemically converts a chemical side chain to a hydroxyl group. Immunity may be natural or acquired.
3the antibiotic susceptibility profile of the microorganism causing the infection. Encyclopedia of Virology Third Edition 2008. Increase in C-reactive protein CRP b.
False More questions like this When a patients immune system reacts adversely to a drug this serious side effect is called a superinfection. Please choose the statement that best describes the benefits of microbial antagonism to the human host. Microbe enters the body and remains confined to a specific tissue.
Please choose the statement that best describes superinfection. A strong superinfection resistance due to blockage or loss of viral receptors develops soon after infection and prevents accumulation of proviruses by reinfection. Superinfection sooper-in-fekshun a new infection occurring in a patient having a preexisting infection.
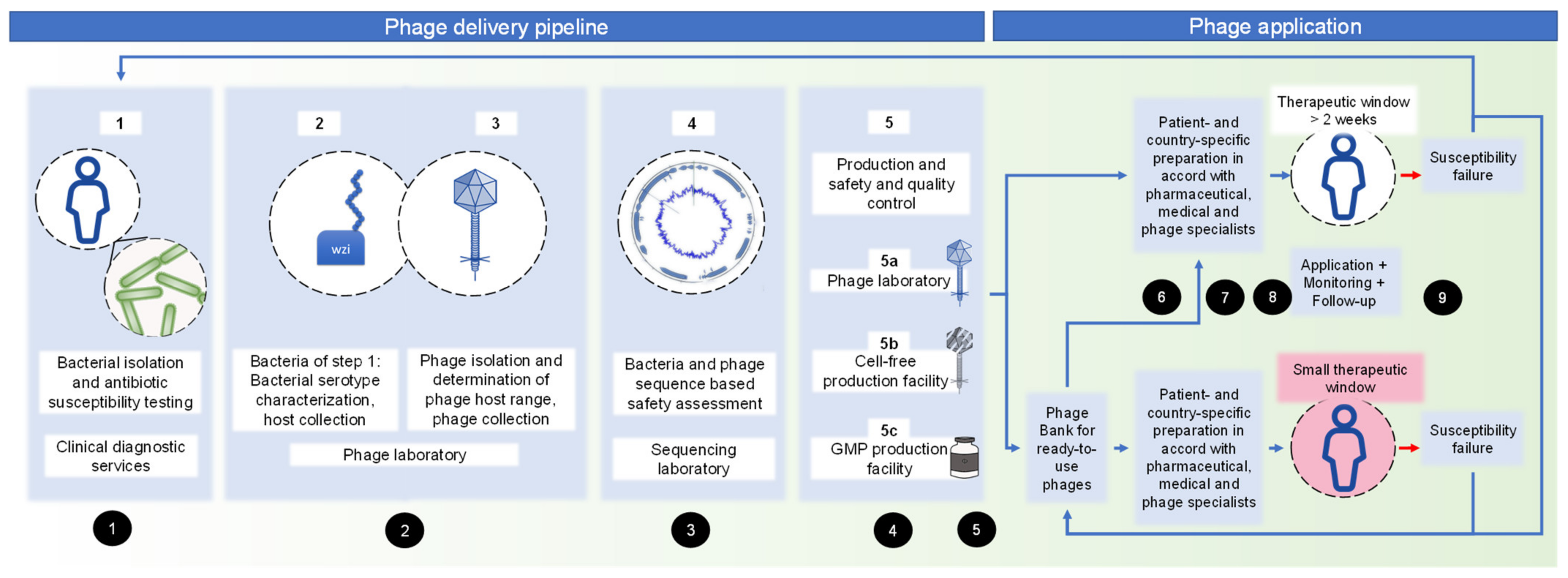
Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text Practical Assessment Of An Interdisciplinary Bacteriophage Delivery Pipeline For Personalized Therapy Of Gram Negative Bacterial Infections Html

Pdf Rates Of Hiv 1 Superinfection And Primary Hiv 1 Infection Are Similar In Female Sex Workers In Uganda
Pdf Co Infection And Super Infection Models In Evolutionary Epidemiology
0 Comments